| [1] Kassem M. Mesenchymal stem cells: biological characteristics and potential clinical applications. Cloning and stem cells.2004;6(4): 369-374. [2] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science.1997;276(5309): 71-74.[3] McCulloch CA. Progenitor cell populations in the periodontal ligament of mice. Anat Rec.1985;211:258-262.[4] Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet.2004;364:149-155.[5] Seo BM, Miura M, Sonoyama W, et al. Recovery of stem cells from cryopreserved periodontal ligament.J Dent Res.2005; 84: 907-912.[6] Liu Y, Zheng Y, Ding G, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cell-mediated treatment for periodontitis in miniature swine. Stem Cells.2008;26:1065-1073.[7] Ding G, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Allogeneic periodontal ligament stem cell therapy for periodontitis in swine. Stem Cells. 2010; 28:1829-1838.[8] Xu J, Wang W, Kapila Y, et al. Multiple differentiation capacity of STRO-1+/CD146+ PDL mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev.2009;18:487-496.[9] 常秀梅,刘宏伟,金岩.牙周膜干细胞的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(7):440-441.[10] 贺慧霞,刘洪臣.干细胞与牙周组织工程研究现状和展望[D] 全军生物医学博士后论坛学术论文集,2009:131-137.[11] 章静波,宗书东,马文丽.干细胞[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2003:137-141.[12] 唐亮,金岩.影响牙周膜干细胞功能的重要因素[J] 实用口腔医学杂志,2009,25(5):737-740.[13] Scadden DT.The stem-cell niche as an entity of action. Nature. 2006;441(7097): 1075-1079.[14] Moore KA, Lemischka IR. Stem cells and their niches. Science. 2006;311(5769): 1880-1885.[15] Chen XD, Fisher LW, Robey PG, et al. The small leucine-rich proteoglycan biglycan modulates BMP-4-induced osteoblast differentiation. FASEB J.2004;18:948-958.[16] Chen XD, Bian X, Teslovich TM, et al. Dissection of the sets of genes that control the behavior of biglycan-deficient pre-osteoblasts using oligonucleotide microarrays. Bone. 2005; 37:192-203.[17] Bi Y, Stuelten CH, Kilts T, et al. Extracellular matrix proteoglycans control the fate of bone marrow stromal cells. J Biol Chem.2005;280:30481-30489.[18] Chen XD, Dusevich V, Feng JQ, et al. Extracellular matrix made by bone marrow cells facilitates expansion of marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells and prevents their differentiation into osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res.2007; 22:1943-1956.[19] Lai Y, Sun Y, Skinner CM, et al. Reconstitution of marrow-derived extracellular matrix ex vivo: a robust culture system for expanding large-scale highly functional human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.2010;19: 1095- 1107.[20] Chen XD. Extracellular matrix provides an optimal niche for the maintenance and propagation of mesenchymal stem cells.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010;90:45-54.[21] Sun Y, Li W, Lu Z, et al. Rescuing replication and osteogenesis of aged mesenchymal stem cells by exposure to a young extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 2011; 25(5): 1474-1485.[22] Joseph J, Kapila YL, Hayami T, et al. Disease-associated extracellular matrix suppresses osteoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells via MMP-1. Calcif Tissue Int.2010;86:154-162.[23] 贺慧霞,刘洪臣,王东胜,等.牙周膜干细胞的表型分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2011, 12(5): 257-260.[24] Desvarieux M,Demmer RT,Rundek T,et al.Relationship between periodontal disease,tooth loss,and carotid artery plaque: the Oral Infections and Vascular Disease Epidemiology Study (INVEST).Stroke.2003:34(9):2120-2125.[25] Amar S, Chung KM, Nam SH, et al. Markers of bone and cementum formation accumulate in tissues regenerated in periodontal defects treated with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membranes. J Periodontal Res. 1997; 32:148-158.[26] Baksh D, Song L, Tuan RS. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(3): 301-316.[27] Kim J, Kang JW, Park JH, et al. Biological characterization of long-term cultured human mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Pharm Res.2009;32(1): 117-126.[28] Izadpanah R, Kaushal D, Kriedt C, et al. Long-term in vitro expansion alters the biology of adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer res.2008; 68(11): 4229-4238. [29] Fuchs E, Tumbar T, Guasch G. Socializing with the neighbors: stem cells and their niche. Cell.2004;116(6): 769-778.[30] Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell.2006;126:677-689.[31] Chen SC,Marino V,Gronthos S,et al.Location of putative stem cells in human periodontal ligament.J Periodont Res.2006; 41(6): 547-553.[32] 高秦,刘宏伟,金岩,等.人牙周膜干细胞的体外分离、纯化及初步鉴定[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2006,22(1):34-37.[33] 申涛,常慧君,简从相,等.改良法分离培养人牙周膜干细胞[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2011, 29(1): 71-74.[34] 甄蕾,刘宏伟.人牙周膜干细胞的初步鉴定及体外成骨诱导[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2008, 18(5): 318-322.[35] SITU Zhen-qiang, WU Jun-zheng. Cell culture[M]. Xi’an: World Publishing Corporation.2007:249-251.[36] 刘娟,赵红宇,人牙周膜细胞群多向分化潜能的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(2):185-189.[37] 闫福华,郑碧琼,林敏魁,等.组织工程用于修复慢性牙周组织缺损的动物实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2005,21(6):593-597.[38] Ivanovski S, Haase HR, Bartold PM. Expression of bone matrix protein mRNAs by primary and cloned cultures of the regenerative phenotype of human periodontal fibroblasts. J Dent Res. 2001;80(7): 1665-1671.[39] Taba M Jr, Jin Q, Sugai JV, et al. Current concepts in periodontal bioengineering. Orthod Craniofac Res.2005; 8(4):292-302. |
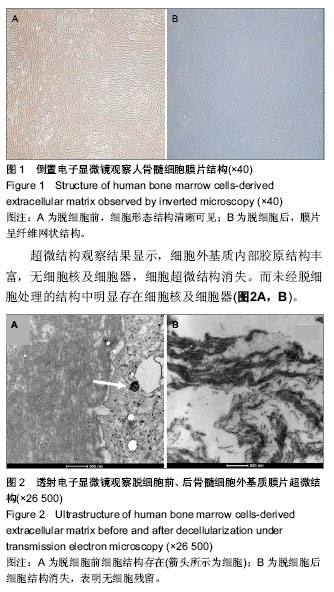
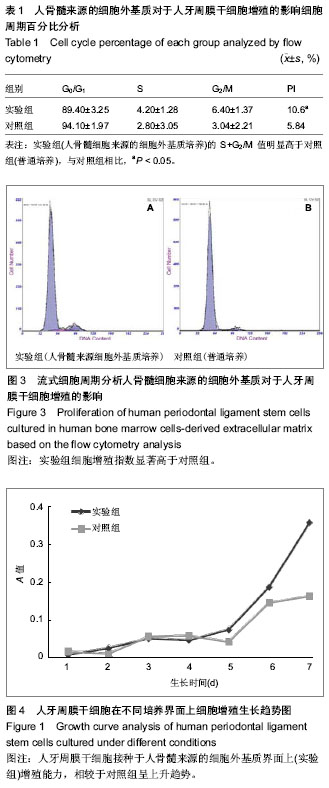
.jpg)